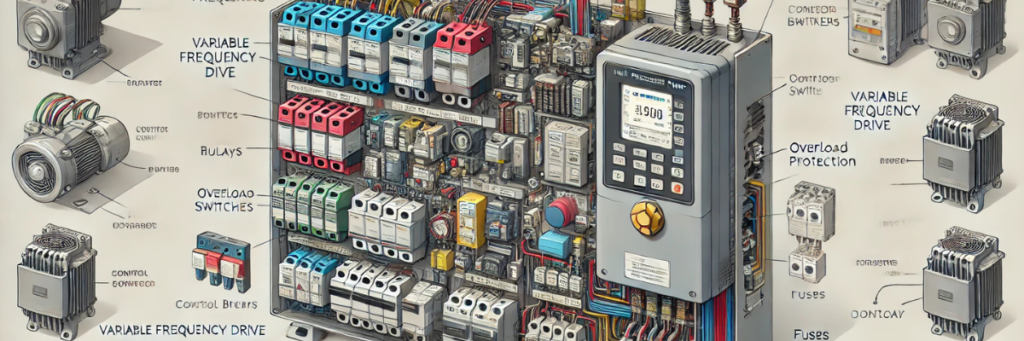
A Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) control panel is essential for managing high-pressure pumps efficiently and ensuring smooth, energy-saving operations. Below is a detailed breakdown of the key components and their functions in a well-designed high-pressure pump VFD control panel.
1. Variable Frequency Drive (VFD)
- Function: Controls motor speed by adjusting the frequency of electrical power.
- Key Features: Overload protection, adjustable speed control, energy efficiency, fault diagnostics.
- Use Case: Prevents motor wear and optimizes energy usage in industries like water treatment, oil & gas, and HVAC systems.
2. Circuit Protection (Breakers & Overload Relays)
- Circuit Breaker:Protects the system from overcurrent and faults
- Overload Relay: Prevents motor overheating and damage
3. Contactors & Control Relays
- Purpose: Manages electrical connection between the VFD and motor for smooth start/stop.
- Automation Role: Enables remote control and can be integrated with PLCs for smart control.
4. Input and Output Filters
- Input Filters: Reduce harmonics and prevent EMI (electromagnetic interference) from power supply.
- Output Filters: Reduce voltage spikes, protecting the motor from damage.
- Best Practices: Use line reactors to further stabilize voltage flow.
5. Control Transformer
- Function: Steps down high voltage for safe operation of control component
- Common Usage: Powers relays, sensors, and communication modules.
- Selection Tip: Choose a shielded transformer for enhanced noise reduction.
6. Cooling & Environmental Control
- Purpose: Protects the motor by disconnecting the circuit when it senses excess current, which could indicate overload conditions.
- Adjustability: Set to the motor’s rated current, providing an additional safety layer for motor protection.
7. Cooling Fans and Heaters
- Cooling Fans: Prevent overheating within the panel due to the heat generated by the VFD and other components.
- Panel Heater: Helps maintain a stable temperature to prevent condensation and potential electrical issues in cooler environments.
8. Human-Machine Interface (HMI) or Display
- Purpose: Displays real-time data such as frequency, voltage, and fault diagnostics.
- Types: Digital LED display or touchscreen interface.
- Enhancement: Use an HMI with alarm indicators for quick troubleshooting.
9. Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) & Smart Control
- PLC Role: Automates pump operation based on sensor feedback.
- Alternative: If a full PLC system is not needed, control relays can handle basic automation.
- Use Case: PLCs in municipal water supply systems ensure steady pressure levels.
10. Current and Voltage Sensors
- Current Transformer (CT): Measures the current flowing to the motor to monitor and protect against overcurrent conditions.
- Voltage Sensor: Monitors voltage levels to ensure stable operation and prevent issues from voltage fluctuations.
11. Safety & Protection Mechanisms
- Emergency Stop Button: Provides an instant shutdown for safety compliance.
- Surge Protection Device (SPD): Protects against power surges and spikes.
- Enclosure Design: Ensure IP-rated enclosures for dust and water protection
12. Surge Protection Device (SPD)
- Function: Protects the VFD and other sensitive components from power surges and spikes that could damage the system.
13. Wiring and Terminal Blocks
- Terminal Blocks: Used for organized connections and easy maintenance of power, control, and communication lines.
- Quality Wiring: Essential for minimizing voltage drops and ensuring safety and efficiency.
Optional Components
- Communication Modules: For remote monitoring and control via protocols like Modbus, Ethernet, or Profibus.
- Battery Backup (UPS): Provides temporary power during outages, allowing for safe shutdown of the system.
A well-designed high-pressure pump VFD control panel with these components will provide efficient control, protection, and operational flexibility, making it essential for applications requiring reliable high-pressure pumping.